In an increasingly interconnected world, the security of network infrastructures has become paramount for both organizations and individuals. One effective solution for bolstering this security is the implementation of an IP Access Controller. This sophisticated technology acts as a gatekeeper, controlling and monitoring access to network resources based on IP addresses, thereby enhancing overall network integrity. With the surge in cyber threats and unauthorized access attempts, understanding the role and functionality of an IP Access Controller is crucial for safeguarding sensitive data and ensuring uninterrupted operations.
An IP Access Controller not only provides a barrier against unwanted intrusions but also allows for the customization of access rights tailored to specific users or devices. By leveraging this technology, organizations can effectively manage permissions, track user activity, and mitigate potential risks associated with unauthorized access. As we delve deeper into the various functionalities and benefits of IP Access Controllers, it becomes clear that they are indispensable tools for any robust security strategy, ensuring that only verified entities can interact with critical network resources.
As the digital landscape continues to evolve, staying ahead of potential vulnerabilities is essential. The deployment of an IP Access Controller is a proactive measure, enabling businesses and individuals to fortify their defenses against a myriad of cyber threats. In the following sections, we will explore the core features of IP Access Controllers, their operational mechanics, and the significant advantages they confer in enhancing network security.

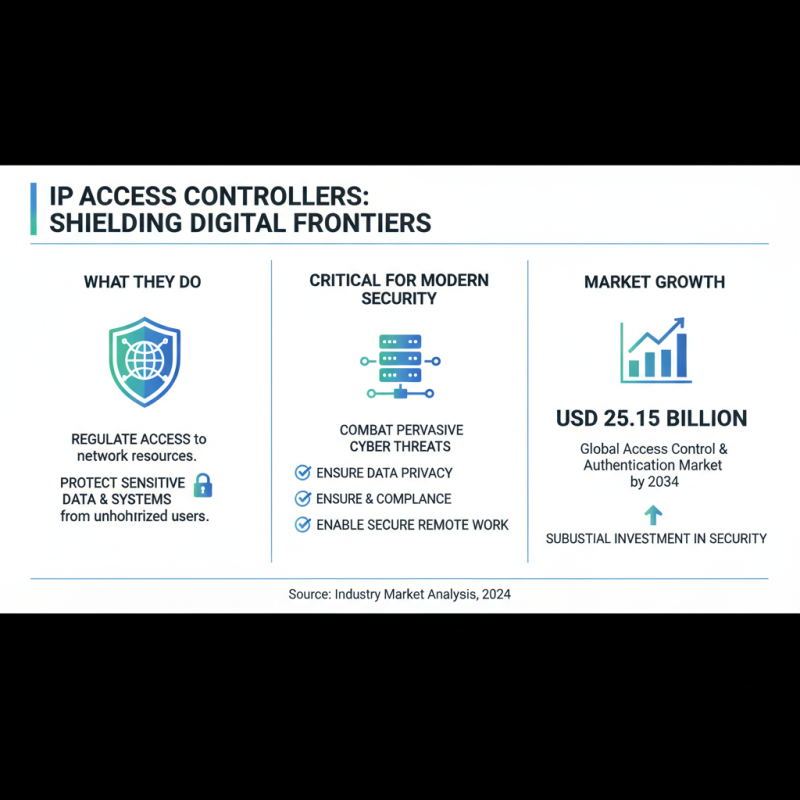
IP access controllers play a vital role in modern network security by regulating who can access network resources. They help organizations protect sensitive information and systems from unauthorized access, which is increasingly critical in an age where cyber threats are pervasive. The global access control and authentication market is expected to grow significantly, reaching a valuation of approximately USD 25.15 billion by 2034, indicating a substantial investment in bolstering security measures across various sectors.
Advancements in technology, including biometric access control systems, are shaping the future of security. Market analysis estimates the size of the global fingerprint access control system market will expand from USD 4.6 billion in 2025 to USD 11.8 billion by 2034. This surge reflects a growing reliance on biometric solutions as a more secure alternative to traditional password-based systems. As organizations continue to prioritize security, the implementation of innovative access control measures, such as attribute-based access control, becomes essential to streamline operations and enhance overall security frameworks.
IP Access Controllers play a crucial role in enhancing network security by implementing various core functions designed to monitor and control access to sensitive information and resources. One of the primary functions is the management of IP addresses, which helps in filtering and blocking unauthorized access attempts. According to a report by Gartner, companies that deploy IP Access Controllers can reduce their risk of data breaches by up to 40%, illustrating how vital this technology is in the current cybersecurity landscape.
In addition to access control, these systems often include advanced authentication methods, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), which significantly bolsters security. A study conducted by Cybersecurity Ventures found that businesses employing MFA experience 99.9% fewer account takeover attacks. Furthermore, IP Access Controllers facilitate real-time monitoring and logging of network traffic, which allows organizations to identify and respond to potential threats promptly. The integration of these features not only protects sensitive data but also ensures compliance with various regulatory standards, emphasizing the importance of IP Access Controllers in today's digital environment.
Implementing IP access controllers in organizations presents numerous advantages that significantly bolster network security. One of the primary benefits is the ability to manage and restrict access to sensitive information and systems. By allowing only authorized IP addresses to connect to the network, organizations can effectively mitigate the risks associated with unauthorized access and potential data breaches. This level of control ensures that sensitive resources are only available to trusted users, reducing the attack surface for malicious actors.
Moreover, IP access controllers enhance the overall visibility of network activity. They enable organizations to monitor and log access attempts, providing valuable insights into who accessed the network and when. This capability not only aids in identifying suspicious behavior but also assists in compliance with regulatory requirements. By maintaining detailed logs of network activity, organizations can demonstrate their commitment to securing data and protecting user privacy. As a result, implementing IP access controllers represents a proactive approach to strengthening network defenses in an increasingly complex threat landscape.
IP Access Controllers are essential tools for enhancing network security, offering various features and technologies that help organizations safeguard their digital assets. One common feature is user authentication, which ensures that only authorized individuals can access specific network resources. This is often achieved through methods such as username and password combinations, biometric verification, or two-factor authentication, adding layers of security against unauthorized access.
Another key technology utilized by IP Access Controllers is IP filtering. This allows network administrators to specify which IP addresses can access the network, thereby preventing potential threats from unrecognized sources. Additionally, many controllers incorporate logging and monitoring capabilities, enabling continual oversight of network activities. This feature helps identify suspicious behavior in real-time, allowing for prompt responses to potential security breaches. Overall, these advanced functionalities significantly strengthen an organization’s defenses against cyber threats.
| Feature | Description | Technology Used | Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Access Control Lists (ACLs) | Rules that define which users have access to specific resources. | Packet Filtering Technology | Enhances network security by limiting access to sensitive data. |
| Authentication Mechanisms | Methods for verifying the identity of users or devices. | RADIUS, TACACS+ | Prevents unauthorized access to the network. |
| Encryption | Protects data in transit by converting it into a secure format. | SSL/TLS, IPsec | Secures sensitive data from interception during transmission. |
| Logging and Monitoring | Tracks user activity and access attempts. | SIEM Solutions, Syslog Servers | Allows for real-time detection of suspicious behavior. |
| Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) | Monitors network traffic for malicious activity. | Signature-Based, Anomaly-Based | Enhances threat detection capabilities within the network. |
Configuring and maintaining IP access controllers (IPACs) effectively is crucial for enhancing network security. One best practice is to implement a strong authentication method. According to a report by Cybersecurity Ventures, 80% of data breaches are due to weak or stolen passwords. Utilizing two-factor authentication (2FA) considerably mitigates this risk, ensuring that only authorized personnel can access sensitive network resources.
Regularly updating firmware and security patches is another essential practice. The Ponemon Institute's Cost of a Data Breach Report 2023 highlights that organizations with unpatched vulnerabilities incur an average breach cost of $4.35 million. Keeping IPACs up-to-date not only protects against known exploits but also boosts overall device performance.
Additionally, logging and monitoring access attempts can provide valuable insights into potential threats. Establishing a robust audit trail enables organizations to respond swiftly to suspicious activities, reinforcing their security posture. By adhering to these best practices, organizations can significantly reduce their risk profile and safeguard their networks against evolving threats.

